Why CFOs Are Cutting AI Budgets (And The 3 Metrics That Save Them) via @sejournal, @purnavirji
Stop measuring AI by hours saved and start measuring the expansion,…

Google’s New User Intent Extraction Method via @sejournal, @martinibuster
Google's user intent extraction research shows how AI on mobile…

Le netlinking est-il mort ? « Ça dépend. »
Ça dépend.
…
 https://blog.c-serp.fr/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2026/01/growthisland-personnes-autour-table-sKIf3L.webp
1080
1080
Hervé @ C-SERP
https://blog.c-serp.fr/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2022/01/Logo-C-SERP-Blog-Storytelling-SEO.png
Hervé @ C-SERP2026-01-26 11:26:102026-01-26 11:26:10Rendez-vous le 5 mars pour le Growth Island 2026 !
https://blog.c-serp.fr/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2026/01/growthisland-personnes-autour-table-sKIf3L.webp
1080
1080
Hervé @ C-SERP
https://blog.c-serp.fr/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2022/01/Logo-C-SERP-Blog-Storytelling-SEO.png
Hervé @ C-SERP2026-01-26 11:26:102026-01-26 11:26:10Rendez-vous le 5 mars pour le Growth Island 2026 !
Google Messages rejoint la famille des User-Triggered Fetchers
Google vient d'ajouter un nouveau crawler à sa documentation…

10 Remarketing Lists To Boost PPC Performance via @sejournal, @brookeosmundson
Turn first-party data into measurable PPC gains using remarketing…
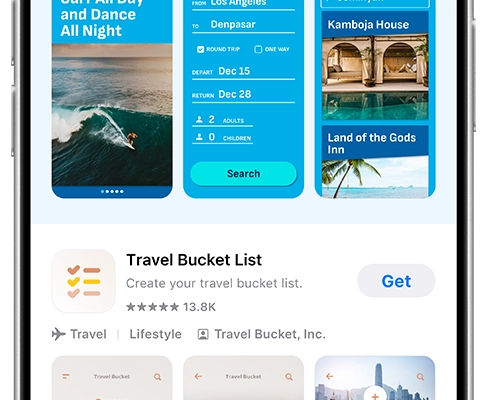
Apple Ads adds more ad slots to App Store search results
Apple is expanding ads in App Store search results, giving advertisers…

The URL mistake that killed Black Friday ft Nick Handley
On episode 338 of PPC Live The Podcast, I speak to Nick Handley…
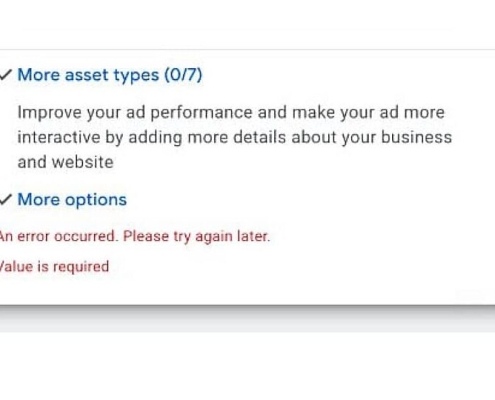
Google Ads bug removes notes option for some advertisers
Some Google Ads advertisers are seeing a bug that causes the…

Google Ads bug blocks edits to Performance Max asset groups
A new bug in Google Ads is preventing some advertisers from…

